Mathematics to grasp mind asymmetry | Coffee and theorems | Science | EUROtoday
Many advances in neuroscience got here due to cautious mathematical evaluation. For instance, Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley used differential equations to explain the motion potential, which transmits data between neurons, which earned them the Nobel Prize in 1963. It is now more and more widespread to make use of mathematical instruments to research large quantities of information. neural pathways which can be being obtained. Beyond this, utilizing basic mathematical rules, it has been attainable to assist conjectures in regards to the functioning of the mind which were put ahead for many years or centuries.
These are related hypotheses with broad assist in the neighborhood, regardless of including little empirical proof or the truth that there are nonetheless no definitive mathematical arguments. They are paying homage to well-known conjectures—corresponding to Fermat's final theorem or the Riemann speculation—that problem a number of generations looking for rigorous affirmation.
An instance is the predictive mind speculation: a lot of our cognitive skills consequence from an evolutionary stress to anticipate our surroundings. The nice success of the calls massive language fashions (LLM), corresponding to OpenAI's ChatGPT or Meta's LlaMa, helps this concept. Their spectacular “intelligence” outcomes from a single activity: maximizing the likelihood of getting the subsequent phrase proper, given an incomplete textual content. This exhibits that prediction permits the event of superior cognition. It stays to be identified whether or not, as well as, cognitive skills at all times require this sort of talent.
Another instance that has simply gained mathematical assist is the speculation that larger cognitive complexity results in lateralization, or breaking the mirror symmetry of the mind. This concept has been accepted nearly because the starting of neuroscience (reaching textbooks and well-liked science books). More than 150 years in the past, the invention of Broca's space (accountable for language technology) confirmed two related information in regards to the mind: that there’s localization (that’s, completely different areas implement completely different duties) and that it’s uneven, since this space It is often situated within the left hemisphere. This led to the postulation that lateralization outcomes from superior human intelligence. Over time, examples of asymmetry have been found in lots of different species, softening the speculation: larger cognitive complexity exerts evolutionary stress in the direction of mind lateralization.
Until lately this was solely supported by anecdotal observations. More empirical proof is troublesome to acquire as a result of problem of measuring mind asymmetry and quantifying cognitive complexity. Furthermore, there was no ample theoretical framework that might enable us to pose—not simply reply—the conjecture in a rigorous method.
A brand new work revealed in Physical Review X gives this framework and supplies a sturdy mathematical argument that helps the speculation. To do that, a mathematical mannequin is used, impressed by the science of advanced methods, during which neural modules and circuits are diminished to summary models. These models encapsulate the complexity of rising cognition, the likelihood that neural circuits make errors, and the prices of utilizing these circuits, such because the metabolic expense of coordinating each hemispheres, or the power dissipated by any irreversible operation.
The key to the mathematical argument lies in a battle between the so-called logical operators, mathematical expressions whose result’s a Boolean worth (true or false). We begin from a easy cognitive activity, which could be solved with an irreducible neural circuit—that’s, it can’t be decomposed into subtasks. The mind may use a single copy of this circuit, situated in a single hemisphere or the opposite (to which the logical operator is assigned XOR); use two coordinated copies of the identical circuit, every situated in a hemisphere (to which the expression AND); or some intermediate mixture (OR). The first choice is cheaper, however the second could also be extra strong in opposition to neuronal failures.
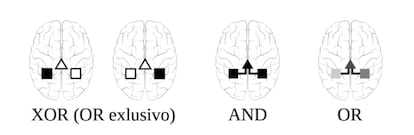
With all attainable configurations, a utilitarian calculation is carried out that takes into consideration prices and advantages. This permits a map to be created that particulars when lateralized options are most well-liked over symmetrical ones based mostly on the mannequin parameters, that are prices and an error price. A primary result’s that there aren’t any intermediate configurations: there’ll at all times be bilaterality or a complete break in symmetry.
A second consequence, and with it the answer to the central speculation, seems when contemplating advanced cognitive duties. In the mannequin, these consist of varied subtasks and require composite circuits to be applied. This leads to an operation AND recursive: to learn from superior cognition it’s essential to implement with out error a subtask, and one other, and one other, and many others. By introducing this new operator within the utilitarian calculation, the map is altered: areas that beforehand demanded bilaterality start to favor lateralization, forcefully exhibiting the existence of evolutionary pressures to lose mind symmetry as cognitive complexity will increase.
A area additionally seems that prefers lateralization for easy duties, however requires duplicate circuits for advanced duties. Thus, cognitive complexity can promote the evolution of recent redundancies, functioning as an evolutionary engine that generates or breaks symmetries in complementary circumstances. The mathematical framework signifies when every chance will happen, in accordance with the metabolic expenditure of the neuronal substrate, its error price and the complexity of the contemplated activity.
These mathematical circumstances, and the inescapable construction of sure summary objects, constrain bodily actuality and the organic materialization of our cognitive skills.
Taking arithmetic significantly, it’s attainable to constrain what designs are attainable and possible on a neural substrate and the corresponding psychological representations. And, as extra empirical proof arrives, this central speculation of neuroscience now rests on a sturdy analytical framework.
Luis F Seoane is a researcher of Higher Council of Scientific Research on the National Center for Biotechnology and a part of Interdisciplinary Group of Complex Systems of Madrid
Agate Rudder G Longoria She is coordinator of the Mathematical Culture Unit of the Institute of Mathematical Sciences (ICMAT)
Coffee and Theorems is a piece devoted to arithmetic and the surroundings during which it’s created, coordinated by the Institute of Mathematical Sciences (ICMAT), during which researchers and members of the middle describe the most recent advances on this self-discipline, share assembly factors between arithmetic and different social and cultural expressions and bear in mind those that marked their improvement and knew find out how to remodel espresso into theorems. The identify evokes the definition of the Hungarian mathematician Alfred Rényi: “A mathematician is a machine that transforms coffee into theorems.”
You can observe MATERIA in Facebook, X e Instagramclick on right here to obtain our weekly publication.
Subscribe to proceed studying
Read with out limits
_
https://elpais.com/ciencia/cafe-y-teoremas/2024-02-01/matematicas-para-entender-la-asimetria-del-cerebro.html
