T Coronae Borealis: A star goes to blow up and will likely be seen to the bare eye very quickly | Science | EUROtoday
Like folks, stars are born, develop and die. And they do it in occasions that trigger giant explosions. A supernova is the dying of a supergiant star, whereas a nova leaves the celebrities alive after shining with a sudden, explosive flash. In basic, these occasions might be tough to foretell, however a minimum of 10 white dwarf techniques are identified to provide novae periodically, 5 of them in our galaxy. This is the case of T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), positioned about 3,000 mild years from Earth. Its historic observations point out that it explodes roughly each 80 years and that cycle is near completion. Once it happens, it will likely be observable to the bare eye as a brand new star within the evening sky.
According to NASA, it is extremely probably that the T CrB two-star system will generate an enormous explosion once more. The final time was in 1946 and a few astronomers had instructed that it’ll achieve this once more between February and September of this yr. However, different specialists want to not enterprise to provide such a detailed estimate. Sumner Starrfield, an astronomer on the University of Arizona who has noticed the habits of the nova, explains relating to the date of the long-awaited occasion: “It could be tonight, this fall, or it could be in 2025 or 2026.
There is no way to determine when it will actually explode. “Our estimates that it will be soon are based on observations of its behavior just before its explosion 80 years ago.” Javier Armentia, astrophysicist and director of the Pamplona Planetarium, agrees not to rush the forecast: “Current behavior gives us clues, but it is not possible to define.”
Every time a brand new star seems within the sky, it’s known as nova —new, in Latin—; though in actuality it’s an astronomical occasion that causes an explosive flash of a star that was already there. T CrB is definitely composed of two stars: a pink large and a white dwarf. The second is a dense stellar core whose gravity attracts the pink large's fuel. The fuel accumulates on the floor of the dwarf till it explodes in an “extremely violent” occasion, as described by Armentia. The star briefly shines extra intensely, and reaches the luminous magnitude of the North Star. Eventually, it returns to regular and the cycle repeats.
Seeing this nova is a as soon as in a lifetime alternative. The dimension disparity between the 2 stars is so nice that it takes the white dwarf 227 days to orbit its pink large, Starrfield explains. They are so shut that matter ejected by the pink large accumulates close to the floor of the white dwarf. Once the roughly Earth-sized mass has gathered within the white dwarf—which takes about 80 years—it turns into scorching sufficient to begin a runaway thermonuclear response. This causes an enormous explosion, as a result of “in a few seconds the temperature increases by 100 to 200 million degrees Celsius,” particulars this astronomer.

A stellar explosion can present itself in a really noticeable manner in house. Depending on the magnitude and distance, the occasion might be noticed with the bare eye or utilizing selfmade telescopes. The T CrB nova will likely be observable with the bare eye. If what occurred in its final explosion is repeated, it will likely be seen for a few week and the system will return to tranquility in a few months: “We will be observing it throughout its evolution,” explains Starrfield.
Novas are uncommon phenomena, so each astronomers think about it will likely be an excellent alternative to broaden data about them. “We don't know much about novae. “Now we have more advanced data and technology than we had in 1946,” describes Armentia. And in line with Starrfield, because of the massive occasion it will likely be potential to learn the way a lot vitality is concerned within the explosion, how a lot of that materials is ejected into house, what the chemical composition of the gases is and the way the massive bang happens.
“Is the gas expelled in a huge cloud? Or in many smaller clouds?” are inquiries to which Starrfield seeks solutions. He is optimistic and assures that there will likely be extra info “that will surprise us.” Thanks to the remark of novae, explains Starrfield, indications have been discovered that a part of the fabric from which the photo voltaic system was shaped might have been produced in nova explosions. “We are pretty sure that the lithium in the solar system comes from nova explosions that occurred before the formation of the solar system,” he explains. Normal novae explode “perhaps every 100,000 years,” he provides. But recurring novae repeat their bursts in a human span because of a peculiar relationship between their two stars.
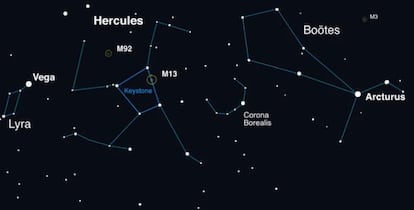
It is a minimum of the third time that humanity has witnessed the T CrB nova, formally found by the Irishman John Birmingham in 1866, after which when it reappeared in 1946. While ready for it to make an enormous explosion once more, astronomers invite to turn into acquainted with the constellation of the Corona Borealis, or Northern Crown, which is a small semicircular arc between the star Arthur—one of many brightest and best to find—and the constellation of Hercules. “That is where the burst will appear as a bright new star,” clarify NASA specialists.
Starrfield's workforce has booked time on the house telescope James Webb to watch the eruption, however this will likely be simply one among many eyes turned towards the outbreak as soon as it begins. Such superior expertise is just not essential to witness this extraordinary occasion as soon as it happens. The star will likely be seen to the bare eye for a few week; and with binoculars, for a month. You simply have to exit and take a look at the Corona Borealis constellation.
You can observe MATERIA in Facebook, X e Instagramclick on right here to obtain our weekly e-newsletter.
https://elpais.com/ciencia/2024-05-28/una-estrella-va-a-explotar-y-podra-verse-a-simple-vista-muy-pronto.html
