How rapidly are costs rising? | EUROtoday
 BBC
BBCPrices within the UK rose by 2.6% within the 12 months to March, lower than within the earlier month however nonetheless above the Bank of England’s goal.
The Bank of England strikes rates of interest up and all the way down to attempt to maintain inflation at 2%, and has minimize charges twice in 2025, taking charges to 4.25%.
The Bank beforehand warned that it anticipated inflation to rise once more in 2025.
What is inflation?
Inflation is the rise within the value of one thing over time.
For instance, if a bottle of milk prices £1 however is £1.05 a yr later, then annual milk inflation is 5%.
How is the UK’s inflation price measured?
The costs of a whole lot of on a regular basis gadgets, together with meals and gasoline, are tracked by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
This digital “basket of goods” is recurrently up to date to mirror procuring traits, with digital actuality headsets and yoga mats added in 2025, and native newspaper adverts eliminated.

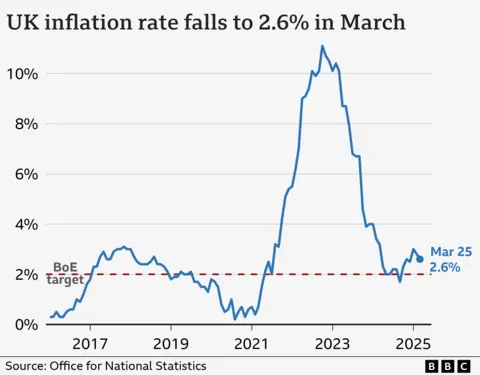
It was an even bigger drop than analysts had anticipated, which the ONS stated was pushed by a fall in clothes and shoe costs.
The Bank additionally considers different measures akin to “core inflation” when deciding whether or not and the way to change charges.
Core CPI does not embody meals or vitality costs as a result of they are typically very risky, so is usually a higher indication of long term traits.
This was 3.4% in March, down barely from 3.5% in February.
Why are costs nonetheless rising?
Inflation has fallen considerably since hitting 11.1% in October 2022, which was the best price for 40 years.
However, that does not imply costs are falling – simply that they’re rising much less rapidly.
Inflation soared in 2022 as a result of oil and gasoline had been in higher demand after the Covid pandemic, and vitality costs surged once more when Russia invaded Ukraine.
It then remained effectively above the two% goal partly due to increased meals costs.
Why does placing up rates of interest assist to decrease inflation?
When inflation was effectively above its 2% goal, the Bank of England elevated rates of interest to five.25%, a 16-year excessive.
The thought is that should you make borrowing dearer, folks have much less cash to spend. People can also be inspired to save lots of extra.
In flip, this reduces demand for items and slows value rises.
But it’s a balancing act – growing borrowing prices dangers harming the financial system.
For instance, householders face increased mortgage repayments, which may outweigh higher financial savings offers.
Businesses additionally borrow much less, making them much less more likely to create jobs. Some could minimize workers and cut back funding.
What is going on to UK rates of interest and can they go down once more?
The Bank of England minimize charges in August and November 2024, and once more in February and May 2025, taking charges to 4.25%.
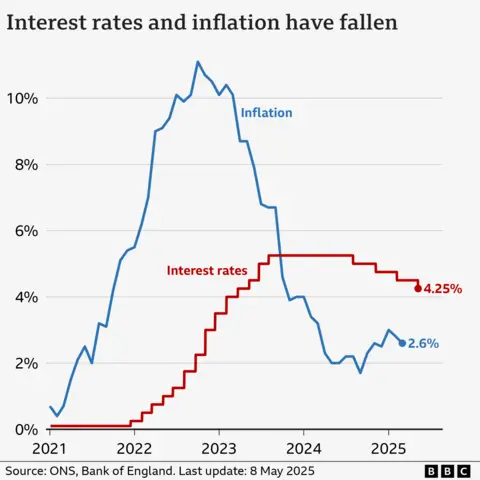
Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey stated the May choice was a results of inflation dropping again, and indicated that additional “gradual and careful” cuts may comply with.
However he warned that the introduction of US tariffs has proven “how unpredictable the global economy can be”. The Bank stated it anticipated the tariffs to sluggish the UK financial system and result in decrease inflation than anticipated.
The Bank beforehand stated it anticipated inflation to spike at 3.7% between July and September 2025 earlier than dropping again in direction of the tip of 2027.
Are wages maintaining with inflation?
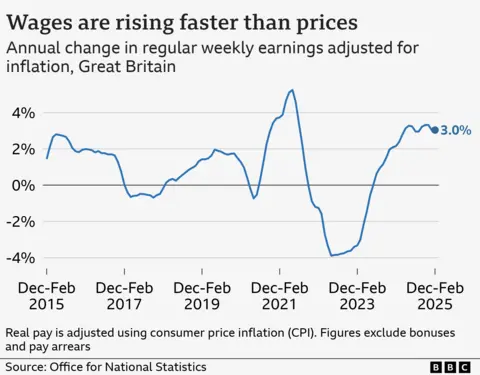
Private sector earnings elevated by greater than public sector pay.
What is going on to inflation and rates of interest in Europe and the US?
The US and EU international locations have additionally been making an attempt to restrict value will increase.
The inflation price for international locations utilizing the euro was 2.2% in April 2025, the identical as in March and down barely from 2.3% in February.
In June 2024, the European Central Bank (ECB) minimize its predominant rate of interest from an all-time excessive of 4% to three.75%, the primary fall in 5 years.
It has since minimize charges an additional 5 instances, taking its key price to 2.5%.
Inflation within the US fell to 2.4% in March, which was down from 2.8% the earlier month however nonetheless above the US central financial institution’s 2% goal.
After a string of cuts within the latter a part of 2024, the US central financial institution once more selected to carry charges at its May assembly, citing the uncertainty generated by the US tariffs.
That leaves its key rate of interest unchanged in a spread of 4.25% to 4.5%.
The Federal Reserve has repeatedly come beneath assault from President Trump, who desires to see additional cuts.
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c17rgd8e9gjo

