More than 3,600 scientists construct a handbook of all human cells: “A Google Maps of biology” | Science | EUROtoday
In science fiction films we’ve got seen how somebody is put right into a machine that scans their cells to detect their illness and treatment it. The robotic physician is a dystopia, however science does aspire to a expertise that might assist actual professionals diagnose any ailment early and precisely, and dictate personalised and precision remedy. Although that may be a very distant aim, right now it’s nearer: a battery of greater than 40 research revealed this Wednesday advances in direction of the development of a 3D atlas of all human cells, an in depth and full digital instruction handbook for the organism.
As with any nice scientific undertaking, the 2016 announcement of the Human Cell Atlas (HCA) was not probably the most talked about information of the day. At that point it began as an formidable initiative, however nonetheless modest in dimension, launched in a presentation in London by 100 scientists led by two biologists, Aviv Regev – right now on the Genentech firm – and Sarah Teichmann – right now on the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute. —. Over the years, the HCA has grown to greater than 3,600 members from 100 international locations, with funding from greater than 100 establishments around the globe. Today it is among the massive international consortiums of what’s generally known as Big Scienceand it’s bigger than what the Human Genome Project as soon as was.
The HCA is organized into 18 networks, every devoted to an organ, tissue or system. Scientists have already characterised greater than 100 million cells from about 10,000 people, taking particular care to make sure that all of the broad human range is represented. Applying precision genomic methods to every particular person cell, along with highly effective bioinformatics and synthetic intelligence (AI) instruments, they examine which of the 20,000 genes of the human genome are lively in every sort of cell, which configures one thing just like the DNI of every mobile profile; what proteins they produce and the way they act, the communication between cells and their structure in tissues, all in detailed navigable spatial maps. In Teichmann’s phrases, it is going to be “a kind of Google Maps of cell biology.”
So far the HCA has offered greater than 440 research, and the info portal already affords atlases of the nervous system, the lung and the attention, which will likely be superimposed on others to type a “complete reference map of the healthy human body,” he summarizes. Teichmann. The atlas not solely covers the grownup organism, but in addition the event of organs and tissues from the embryonic and pediatric levels, which are sometimes the origin of illnesses all through life.
Causes of the illness and new medicine
The greater than 40 research revealed right now in varied magazines of the group Nature They characterize “a crucial moment for the HCA community,” says Regev; an awesome joint push to the undertaking that covers a number of fronts, from the event of the placenta, the skeleton and the nervous system, to the impression of genetic variations on cell ailments, by way of the results of COVID-19 on the lungs or the operate and alterations of the digestive system, amongst different fields.
All of those outcomes will likely be built-in into the primary draft of the HCA, which will likely be revealed in 2025-26, accessible on-line with open entry, and can proceed to develop to incorporate a quantity of billions of cells in every organ and tissues of the human physique, made up of a complete of about 37 trillion cells.
According to Regev, “the main future – and current benefit – is the advance in the discovery of the causes of the disease and the development of medications. “Scientists already use the atlas every day for these purposes.” Thus, explains the co-founder of the HCA, researchers evaluate cells from diseased tissues, equivalent to biopsies of tumors or sufferers with autoimmunity, with wholesome reference cells, and the variations of their composition and expressed genes are clues to the origin. of the illness and its attainable therapies. “At Genentech we have a clinical trial on inflammatory bowel disease that we have undertaken in part thanks to the analysis of large-scale data from the atlas,” highlights the scientist.
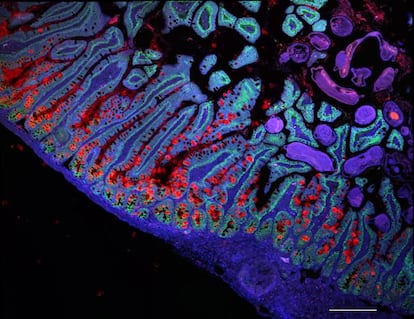
The essay that Regev cites is said to one of many research revealed right now, which identifies a sort of cell concerned in inflammatory bowel ailments equivalent to ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s illness. The research, co-directed by Teichmann and revealed in Natureis a collaboration that features a group of scientists from the Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS) —primarily based on the Hospital Clínic of Barcelona— and the Networked Biomedical Research Center for Liver and Digestive Diseases (CIBEREHD). .
Researchers have collected current sequences of RNA – the product of genes which can be used to create proteins – from particular person cells, together with new samples, bringing collectively a complete of 1.1 million wholesome cells of 137 differing types over a time frame. all the digestive tract, each grownup and growing. The digestive atlas is accomplished with one other half 1,000,000 cells affected by illnesses equivalent to abdomen or colorectal most cancers, celiac illness, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s illness.
Wrong cells in intestinal irritation
By evaluating the transcriptional profiles—the RNAs current within the cells—scientists have noticed within the massive gut of sufferers sure cells just like these within the abdomen or small gut. “The presence of cells that correspond to another tissue is common in the context of chronic inflammation,” says the director of the Spanish group, Azucena Salas. The scientist explains that this had been assigned to the therapeutic of wounds within the intestinal wall, however there’s a new discovering: these inaccurate cells, that are generated from stem cells throughout restore, promote irritation itself. “They are not pure spectators, but rather actively participate in intestinal damage,” says Salas.
According to review co-director Rasa Elmentaite, from the corporate Ensocell Therapeutics, processing the findings from the digestive atlas in AI platforms will assist design a brand new era of therapies. “Despite the critical role of epithelial cells in the progression of inflammatory bowel disease, available treatments do not act effectively on them.”
In these new therapies, organoids will play a central position, miniature variations of organs and tissues which can be already utilized in laboratories to deepen our information of their features and ailments, and to check new medicine. “To know that the organoid correctly represents the organ, we need to compare its cells with a reference atlas of the organ, and the HCA gives us that,” says Regev. On the horizon is the long-awaited promise of regenerative medication: “Understanding normal cellular development helps biomedical engineering create cells that can be introduced into the body as therapy.”
https://elpais.com/ciencia/2024-11-20/mas-de-3600-cientificos-construyen-un-manual-de-todas-las-celulas-humanas-un-google-maps-de-la-biologia.html
