Russian jamming of U.S. weapons in Ukraine forces Pentagon to regulate | EUROtoday
Russia’s skill to fight the high-tech munitions has far-reaching implications for Ukraine and its Western supporters — probably offering a blueprint for adversaries comparable to China and Iran — and it’s a key cause Moscow’s forces have regained the initiative and are advancing on the battlefield.
The success price for the U.S.-designed Excalibur shells, for instance, fell sharply over a interval of months — to lower than 10 % hitting their targets — earlier than Ukraine’s army deserted them final yr, in line with the confidential Ukrainian assessments.
While different information accounts have described Russia’s superior digital warfare capabilities, the paperwork obtained by The Post embody beforehand unreported particulars on the extent to which Russian jamming has thwarted Western weaponry.
“The Excalibur technology in existing versions has lost its potential,” the assessments discovered, including that battlefield expertise in Ukraine had disproved its popularity as a “one shot, one target” weapon — at the very least till the Pentagon and U.S. producers deal with the difficulty.
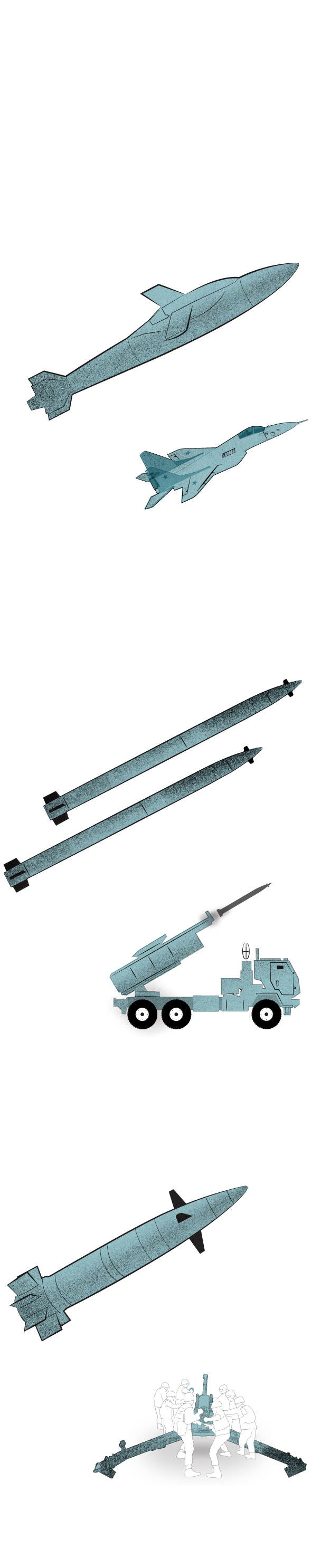

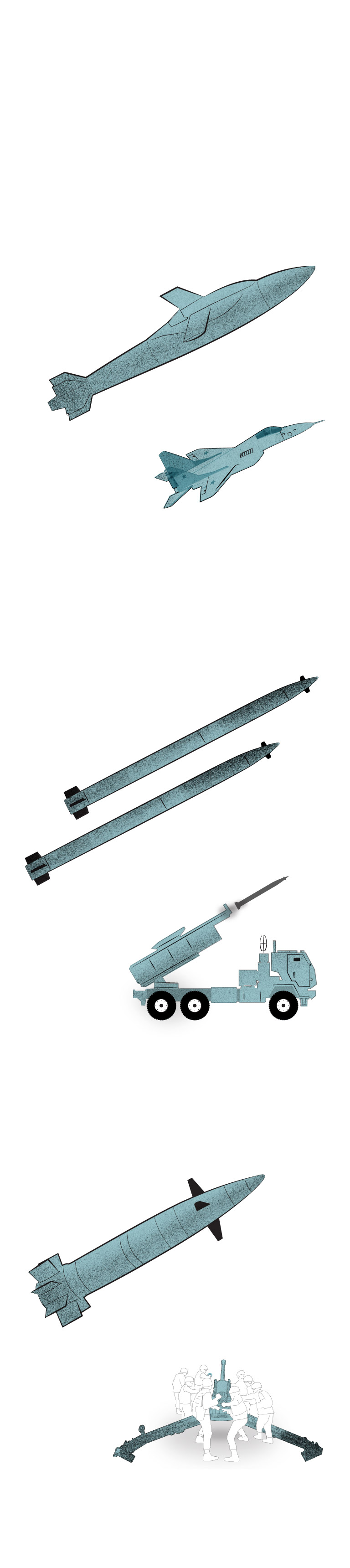
Some of the weapons
affected by Russian jamming
Joint Direct Attack
Munition-Extended Range
Air-launched GPS-guided weapon that converts dumb bombs into precision-guided glide bombs.
Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System
The M142 (pictured) and M270 launch rockets at a spread of about 50 miles. They may fireplace the longer vary ATACMS missiles.
Rounds are guided by GPS coordinates programmed earlier than firing. NATO 155mm howitzers such because the M777 fireplace the weapon.
Note: Illustrations to not scale
Sources: Raytheon, Army Recognition
Some of the weapons
affected by Russian jamming
Joint Direct Attack
Munition-Extended Range
Air-launched GPS-guided weapon that converts dumb bombs into precision-guided glide bombs.
Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System
The M142 (pictured) and M270 launch rockets at a spread of about 50 miles. They may fireplace the longer vary ATACMS missiles.
Rounds are guided by GPS coordinates programmed earlier than firing. NATO 155mm howitzers such because the M777 fireplace the weapon.
Note: Illustrations to not scale
Sources: Raytheon, Army Recognition
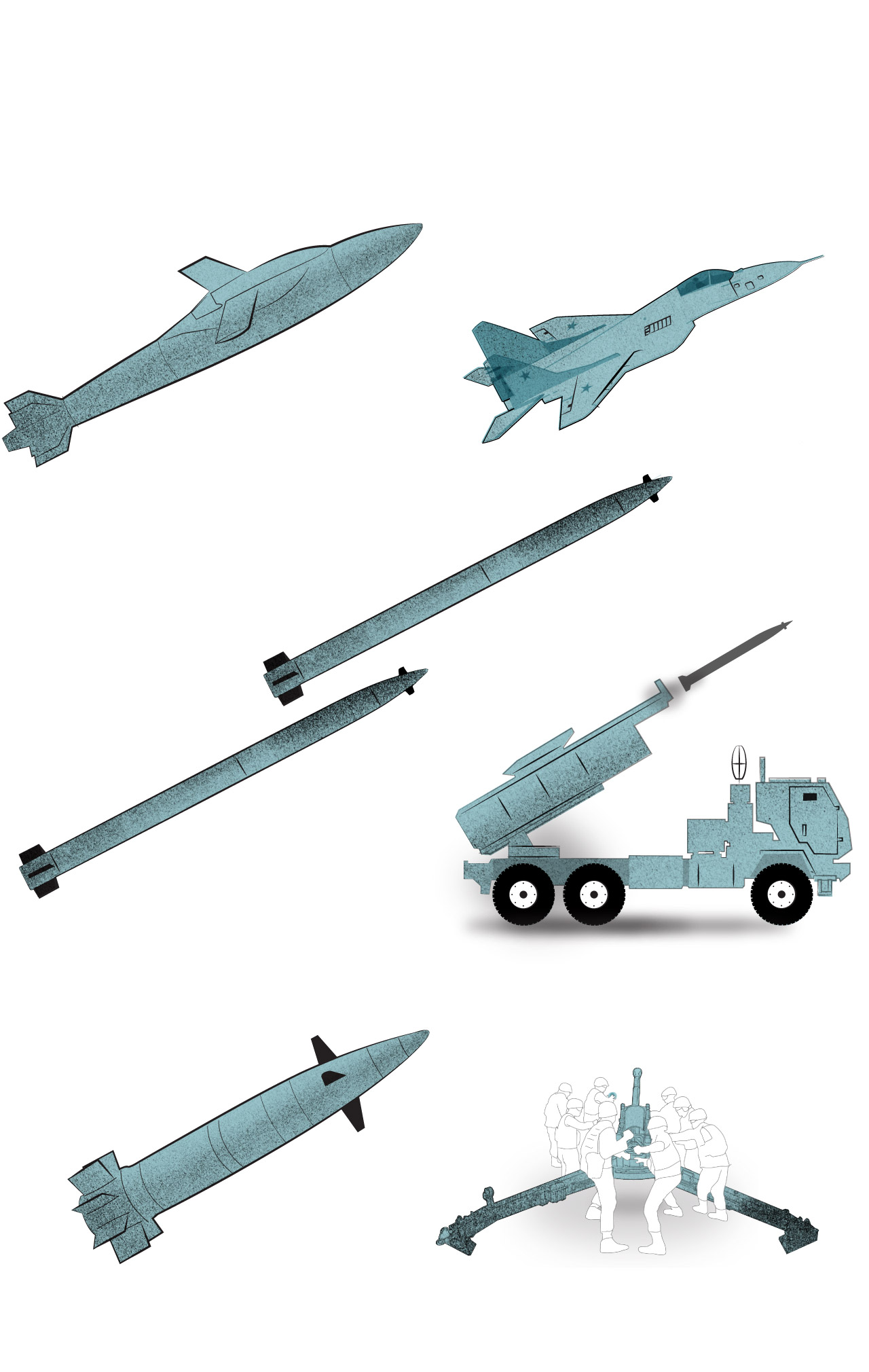
Some of the weapons affected by Russian jamming
Joint Direct Attack Munition-Extended Range
Air-launched GPS-guided weapon that converts dumb bombs into precision-guided glide bombs.
Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System
The M142 (pictured) and M270 launch rockets at a spread of about 50 miles. They may fireplace the longer vary ATACMS missiles.
Rounds are guided by GPS coordinates programmed earlier than firing. NATO 155mm howitzers such because the M777 fireplace the weapon.
Note: Illustrations to not scale
Sources: Raytheon, Army Recognition
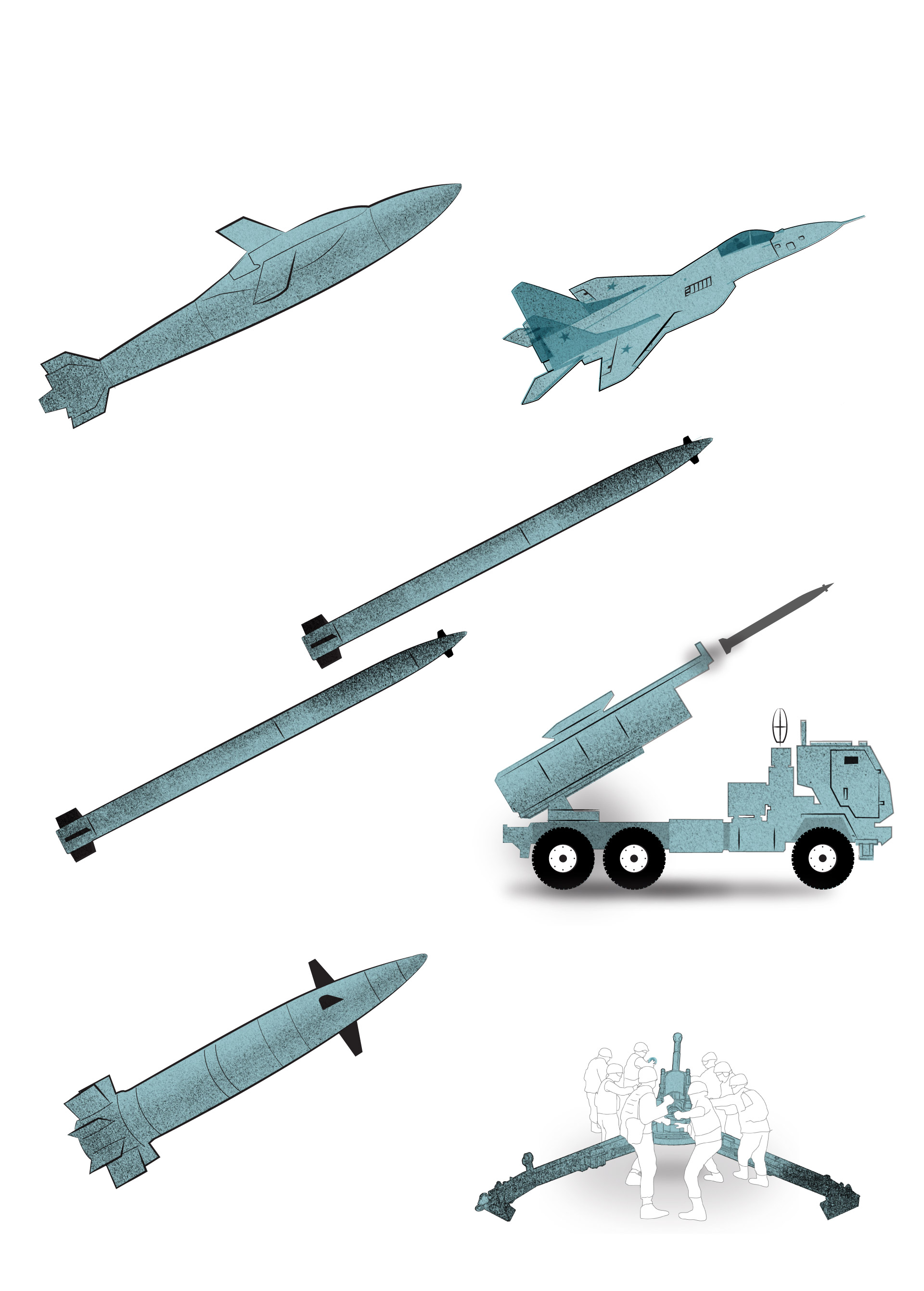

Some of the weapons affected by Russian jamming
Joint Direct Attack
Munition-Extended Range
Air-launched GPS-guided weapon that converts dumb bombs into precision-guided glide bombs.
Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System
The M142 (pictured) and M270 launch rockets at a spread of about 50 miles. They may fireplace the longer vary ATACMS missiles.
Rounds are guided by GPS coordinates programmed earlier than firing. NATO 155mm howitzers such because the M777 fireplace the weapon.
Note: Illustrations to not scale
Sources: Raytheon, Army Recognition
Six months in the past, after Ukrainians reported the difficulty, Washington merely stopped offering Excalibur shells due to the excessive failure price, the Ukrainian officers stated, talking on the situation of anonymity to debate a delicate safety matter. In different circumstances, comparable to aircraft-dropped bombs referred to as JDAMs, the producer offered a patch and Ukraine continues to make use of them.
Ukraine’s army command ready the stories between fall 2023 and April 2024 and shared them with the U.S. and different supporters, hoping to develop options and open up direct contact with weapons producers. In interviews, Ukrainian officers described a very bureaucratic course of that they stated had sophisticated a path towards urgently wanted changes to enhance the failing weaponry.
The officers agreed to reply questions in regards to the assessments in hopes of drawing consideration to the Ukrainian army’s wants. Several Ukrainian and U.S. officers interviewed for this story spoke on the situation of anonymity as a result of sensitivity of the difficulty.
The Pentagon anticipated that some precision-guided munitions can be defeated by Russian digital warfare and has labored with Ukraine to hone techniques and methods, a senior U.S. protection official stated.
Russia “has continued to expand their use of electronic warfare,” the senior U.S. official stated. “And we continue to evolve and make sure that Ukraine has the capabilities they need to be effective.”
The U.S. protection official rejected claims that forms has slowed the response. The Pentagon and weapons producers have offered options typically inside hours or days, the official stated, however didn’t present examples.
Ukraine’s Ministry of Defense, in an announcement, stated that it cooperates commonly with the Pentagon and likewise communicates instantly with weapons producers.
“We work closely with the Pentagon on such matters. In the event of technical problems, we promptly inform our partners to take the necessary measures to solve them in a timely manner,” the ministry stated. “Our partners from the USA and other Western countries provide constant support for our requests. In particular, we regularly receive recommendations to improve the equipment.”
U.S.-made guided munitions offered to Ukraine sometimes have been profitable when launched, however typically grew to become much less in order Russian forces tailored. Now, some arms as soon as thought-about potent instruments now not present an edge.
In a standard warfare, the U.S. army won’t face the identical difficulties as Ukraine as a result of it has a extra superior air drive and strong digital countermeasures, however Russia’s capabilities nonetheless put heavy strain on Washington and its NATO allies to proceed innovating.
“I’m not saying no one was worried about it before, but now they’re starting to worry,” one senior Ukrainian army official stated.
“As we share information with our partners and our partners share with us, the Russians definitely also share with China,” the official added. “And even if they don’t share with China … China monitors events in Ukraine.”
Failing to strike targets
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine created a contemporary testing floor for Western arms that had by no means been used in opposition to a foe with Moscow’s skill to jam GPS navigation.
Innovation is a function of just about each battle, together with the warfare in Ukraine, the place all sides deploys know-how and novel adjustments to outfox the opposite and exploit vulnerabilities. The Russian army has been adept at digital warfare for years, analysts and officers stated, investing in methods that may overwhelm the alerts and frequency of digital parts, comparable to GPS navigation, which helps information some precision munitions to their targets.
Ukrainians initially discovered success utilizing Excalibur 155mm rounds, with greater than 50 % precisely hitting their targets early final yr, in line with the confidential evaluation, which was based mostly on direct visible observations. Over the subsequent a number of months, that dropped under 10 %, with the evaluation pointing to Russian GPS jamming because the wrongdoer.
The examine cautioned that far fewer shells have been fired later within the analysis interval, and plenty of weren’t noticed, leaving the exact success price unclear.
But even earlier than the United States ceased deliveries, Ukrainian artillerymen had largely stopped utilizing Excalibur, the assessments stated, as a result of the shells are more durable to make use of in contrast with normal howitzer rounds, requiring time-consuming particular calculations and programming. Now they’re shunned altogether, army personnel within the discipline stated.
The senior Ukrainian official stated Kyiv shared this suggestions with Washington however obtained no response. The Ukrainians have confronted the same problem with guided 155mm shells offered by different Western nations. Some make use of steering apart from GPS, and it’s unclear why in addition they grew to become much less efficient. U.S. protection officers declined to deal with the Ukrainian assertion.
The Excalibur precision artillery spherical typifies many U.S. weapons: expensive and complex however correct. Ukraine has used the rounds, fired by U.S. artillery methods such because the M777, to destroy targets, like enemy artillery and armored autos, from about 15 to 24 miles away.
Rob Lee, a senior fellow with the Foreign Policy Research Institute, a Philadelphia-based analysis group, stated that Russia’s use of digital warfare to fight guided munitions was an essential battlefield improvement previously yr. Many weapons are potent after they’re launched, however they lose effectiveness over time, Lee stated, a part of a nonstop sport of cat-and-mouse between adversaries who continually adapt and innovate.
The involvement of protection firms is essential to overcoming Russian defenses comparable to jamming, Lee stated.
“The problem with a lot of Western defense companies,” Lee stated, in contrast with Russian producers, is that “there is not the same sense of urgency.”
An internet of Russian digital warfare methods and air defenses menace Ukrainian pilots, the paperwork stated, including that some Russian jammers additionally scramble the navigation system of planes. The Russian protection is so dense, the evaluation discovered, that there are “no open windows for the Ukrainian pilots where they feel that they are not at gunpoint.”
Despite some effort to thwart the jamming, potential fixes appear restricted till the West delivers F-16 fighter jets, the evaluation discovered. Such fashionable planes would permit Ukraine’s air drive to push Russian pilots again, enabling using completely different sorts of weapons with higher vary and talent to keep away from some digital warfare methods.
The aircraft-dropped JDAMs present one other instance of declining effectiveness of weaponry.
Their introduction, in February 2023, was a shock to Russia. But inside weeks, success charges dropped after “non resistance” to jamming was revealed, in line with the evaluation. In that interval, bombs missed their targets from as little as 65 ft to about three-quarters of a mile.
Ukraine offered suggestions in regards to the jamming downside, and the U.S. and weapons producers delivered improved methods in May, the paperwork stated. Since then, JDAMs have proved extra proof against jamming than different GPS-guided weapons, the evaluation discovered, and accuracy improved to successful price above 60 % over 9 months in 2023.
HIMARS have been celebrated throughout the first yr of Russia’s invasion for his or her success in hanging ammunition depots and command factors behind enemy strains.
But by the second yr, “everything ended: the Russians deployed electronic warfare, disabled satellite signals, and HIMARS became completely ineffective,” a second senior Ukrainian army official stated. “This ineffectiveness led to the point where a very expensive shell was used” more and more to strike lower-priority targets.
The Ukrainian army paperwork didn’t assess guided M30 or M31 munitions, that are fired from HIMARS launchers. But in January, Ukraine’s army command wrote a coverage paper urging Western supporters to supply an alternate: M26 cluster munitions that additionally could possibly be launched from multiple-launch rocket methods. These low-tech, unguided rockets are proof against jamming, and the cluster submunitions can nonetheless hit targets in a large space even when the shot is imprecise.
Kyiv nonetheless considers its HIMARS rockets efficient, however Russian jamming may cause them to overlook a goal by 50 ft or extra.
“When it’s, for example, a pontoon bridge … but there’s a 10-meter deviation, it ends up in the water,” the primary Ukrainian official stated.
Russian jamming alerts are despatched up from the bottom and type a cone-shaped space. Any guided munition — or plane — passing by way of is susceptible to interference.
A battalion commander, talking on the situation of anonymity as a result of he was not approved to take action publicly, described flying a reconnaissance drone in foggy circumstances final yr in Bakhmut to trace a HIMARS strike on a Russian place. On his display, the commander watched in dismay as every rocket missed.
One method the Ukrainians counter Russia’s jamming is by concentrating on identified digital warfare methods with drones earlier than utilizing HIMARS. This has proved efficient in some circumstances.
“Initially, there were no problems,” the primary senior official added. “It was simple: the machine arrived. The button was pressed and there was a precise hit. Now, it’s more complicated.”
The official added, “The Americans are equipping HIMARS with additional equipment to ensure good geolocation.”
One U.S. weapon utilized by plane, the GBU-39 small-diameter bomb, has proved resilient to jamming, in line with the confidential paperwork. Nearly 90 % of dropped bombs struck their goal, the evaluation discovered.
Its smaller floor space makes it harder for Russian methods to detect and intercept, the paperwork stated. Ukraine first obtained the aerial weapons, which has not been beforehand disclosed by the Pentagon, in November 2023.
The GBU-39 was additionally tailored for land use in HIMARS methods, a improvement that Pentagon officers stated would enhance the vary of rocket artillery. But the modified weapons, often known as Ground-Launched Small Diameter bombs, or GLSDB, proved ineffective in comparison with these launched from airplanes, Ukrainian officers stated. The floor variations have been examined in Ukraine, one official stated, and the Americans are engaged on changes earlier than offering them anew.
William LaPlante, the Pentagon’s acquisition chief, stated final month that an tailored weapon “didn’t work for multiple reasons,” together with jamming and different tactical and logistical points. LaPlante didn’t disclose which weapon he was referring to, however different specialists stated that he was describing the GLSDB.
“When you send something to people in the fight of their lives,” LaPlante stated, “they’ll try it three times and then they just throw it aside.”
Senior Ukrainian army officers stated Storm Shadow air-launched cruise missiles, offered by Britain, are much less prone to Russian jamming as a result of they don’t rely solely on GPS however two different navigation methods, together with an inner map that matches the terrain of its supposed flight path. Russian air defenses nonetheless have had some success intercepting them.
The Ukrainians have additionally had success up to now with U.S.-provided Army Tactical Missile System long-range missiles, which have a spread of as much as 190 miles, however they, too, could be focused by Russian air defenses.
The Ukrainian officers stated they anticipate that weapons efficient on the battlefield now will equally droop inside a yr.
“The Russians will learn how to fight it,” the second Ukrainian official stated. “That’s how the arms race works.”
Horton reported from Washington.
https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2024/05/24/russia-jamming-us-weapons-ukraine/
